Proof of reserves and liquidity in crypto explained
The cryptocurrency market has not been shielded from the recent macroeconomic influences that have impacted traditional financial markets. War, inflation, and a worldwide pandemic are just some of the factors that have caused turbulence and price volatility in the sector. However, one of the most detrimental elements to the crypto-sphere was self-inflicted, as several exchanges collapsed, causing widespread confusion and distrust. Going forward, a big question is: how do cryptocurrency exchanges rebuild trust? Transparency around reserves is a much-touted solution, but why is it so important? Read on as we explore proof of reserves and liquidity in crypto.
The FTX crash understandably made the existing cryptocurrency community and potential investors apprehensive about what exchanges they trust going forward. Search engine queries for ‘proof of reserves’ and ‘liquidity in crypto’ hit the roof in late 2022, with the public becoming increasingly critical of exchanges, demanding better transparency and more audits of crypto holdings. So, what exactly is proof of reserves?
What is proof of reserves?
Proof of reserves (PoR) is the process of verifying that the customer assets held by a cryptocurrency exchange or financial institution correspond to the number of assets the company holds in reserve on behalf of the customers. PoR has been highly publicised as the primary solution for crypto investors to make sure that their funds are being secured appropriately. It’s also a useful tool for crypto platforms as it provides a way to prove they are solvent i.e. possessing enough assets to cover trades and withdrawals.
PoR is typically executed by a third-party auditor that will analyse the holdings and liabilities of a trading platform. The auditors aim to substantiate the claims made by the exchange and will subsequently publish the results for public consumption. This theoretically ensures that the digital assets held in custody for users by the exchange are backed 1:1 by exchange-owned reserves.
A thorough PoR audit can benefit both crypto platforms and customers as it minimises the likelihood of the exchange disregarding their custodian responsibilities and utilising investor assets for their own purposes, e.g. investing in businesses or loaning user deposits to third parties. In addition, PoR can work to assure customers that the crypto platform is not in jeopardy of experiencing liquidity issues and that their funds are available for withdrawal at any time regardless of wider market conditions.
What’s the difference between an audit and an attestation?
The clamour for crypto exchange audits has been all the rage as of late, with crypto exchanges producing external results for public scrutiny - but do all investigations deliver the same level of detail?
Though similar, PoR audits and attestations offer different services:
Attestation: This refers to official verification that documents, data, or published results are authentic and valid. In cryptocurrency, attestation is a snapshot of liabilities and reserves used primarily to help customers understand the current state of an exchange’s finances. This analysis is based on agreed-upon procedures and parameters set by the client (financial institution) that presents overarching conclusions rather than the opinions and insights of the investigating body.
Audit: This is an objective analysis and evaluation of a company’s financial statements to make sure that the financial records are accurate and valid. In the crypto world, the funds held by an exchange must match or surpass the net value of assets deposited by the customers on the platform. An audit, in this case, is a detailed exploration of an exchange’s balance sheet to corroborate these funds and confirm liquidity.
Attestation refers to verifying official documents and results. An audit is a detailed analysis and the process of verifying claims made by the company. While audits and attestations vary in detail, both are extremely valuable as they help encourage transparency in crypto firms, making it challenging for them to engage in illegal financial practices.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereHow does the auditing process work?
Although there are various cold storage and non-custodial options to secure cryptocurrency, many people choose the crypto custodial storage option to safeguard their assets because centralised platforms offer both convenience and security. Keeping assets on a crypto exchange allows for user flexibility as it’s easier to trade assets quickly. In this case, the exchange acts as a custodian, a third-party security provider that takes possession and secures the private keys that provide access to crypto assets.
The recent high-profile collapses of major crypto platforms, however, have brought the integrity of these custodians into question. To guard against potential misleading claims and ensure the crypto exchange custodians are acting appropriately, PoR audits are employed to ensure that a company’s holdings match the investors’ assets. An independent third-party firm is brought in to conduct these procedures, mitigating any potential fraud or bias.
Here’s how an audit works:
The third-party auditor generates a snapshot of the crypto company’s liabilities, meaning the total amount of customer deposits.
The auditor also verifies ownership of the company's crypto assets. The company provides a digital signature from the private keys corresponding to all its addresses.
Finally, the auditor verifies that the amount of assets exceeds the number of liabilities.
In addition, independent customer verification is another process many exchanges utilise to add further transparency and assure customers that their account is included in the liabilities that are covered by the held assets. Here’s how it works:
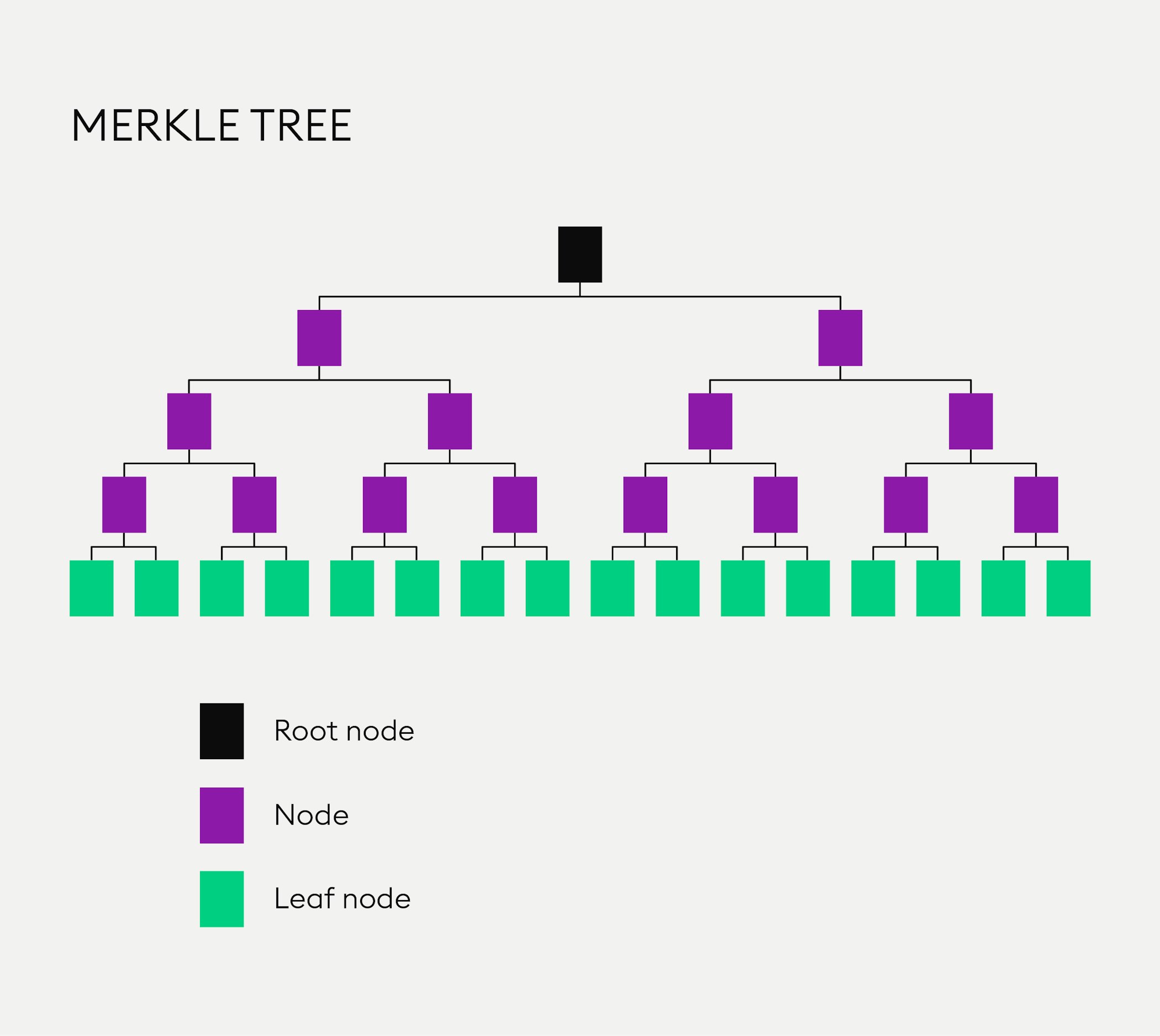
1. The exchange creates a Merkle tree where every customer account is a leaf.
2. An auditor verifies that the Merkle tree includes all liabilities.
3. They provide each customer with their leaf information and a way to verify the path from their leaf to the Merkle root.
What is a Merkle Tree?
A Merkle tree, named after the scientist Ralph Merkle, is a hash-based data formation used in cryptography and computer science. It is a data structure constructed by repeatedly hashing a set of data. With every layer of hashing, the number of data pieces (Merkle leaves), is exponentially reduced until a single hash (Merkle root) is left at the top of the Merkle tree. With Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, all the transactions inside a block are summarised in a Merkle tree by producing a digital fingerprint of the entire set of transactions. This way you can verify whether a transaction is included in a block.
Merkle trees are useful for two key reasons:
1. They provide a single hash for a large set of data, ensuring that none of the included data has been tampered with.
2. They are used to easily verify the inclusion of a single node/leaf in the structure, only needing to provide the path to the root instead of the whole tree.
In relation to PoR, Merkle trees are particularly useful for auditors as it allows them to maintain customer privacy. Auditors can aggregate the data of all user account balances into a single Merkle root without disclosing the account balance of any individual customer.
What is liquidity?
Liquidity is essentially how easy it is for things to be bought and sold without causing a drastic change in an asset's price, and it can refer to both markets and assets. In the crypto world, to ensure that holders can get speedy trades, the market must be liquid, meaning high activity and minimal spread between the bid and ask prices. Furthermore, liquidity can also refer to the ease with which a crypto asset can be exchanged for other tokens or converted into fiat currencies.
In times of high volatility, the crypto market liquidity will be lower because the fluctuating market prices discourage trades, causing buy and sell orders to take longer to fulfil as there is less activity in the market. However, in times of stability, the crypto market will experience high liquidity because more people invest, meaning buy and sell orders are quicker to execute.
Why is market liquidity important?
The investors of the crypto market range from opportunistic day traders to steadfast HODLers, but what they have in common is the desire for a return on investment. Market liquidity is important in the crypto market because it means investors can make quick trades without destabilising a coin or token as there are plenty of buyers willing to purchase or trade the digital asset. This is an example of high market liquidity as the crypto market has a large number of investors and high trade volumes, which means the market is stable. Conversely, low market liquidity means lower trade volumes, fewer investors, and consequent instability in the market. In these conditions, there is more risk of market manipulation because a large purchase or dump of a low-liquidity crypto asset can lead to a snowball effect and massively influence trade patterns going forward.
What is a crypto liquidity crunch?
In the crypto world, a liquidity crisis occurs when an exchange lacks fiat currency or convertible digital assets to facilitate user transactions. As mentioned previously, user funds on crypto platforms are expected to be backed 1:1 by exchange-owned reserves, which should negate any potential liquidity issues. However, problems arise when a wider economic issue like a recession causes people to make sudden trades or large withdrawals due to concerns about the stability of the market. In these extraordinary instances, exchanges may freeze transactions, meaning users cannot trade, convert, or withdraw their assets.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowTransparency and trust with Bitpanda
The crypto market is already on the recovery course from its recent setbacks, however, it’s important to remain vigilant and discerning when it comes to who you trust with your funds. Bitpanda is proud to be recognised as one of the safest and most regulated platforms in Europe. We understand and welcome the increased demand from crypto investors for improved financial transparency across the board. We’re leading the way by actively seeking to be regulated by several jurisdictions.
We also ensure that our funds are regularly reviewed by a third party so that our customers have visibility into our assets and verification that their investments are covered by corresponding crypto funds stored in Bitpanda’s cold wallets. In fact, Bitpanda customers can request the results of previous reports at any time on our website.
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any digital assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in digital assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.