Ethereum 2.0 simply explained
Ethereum 2.0 refers to a set of updates that tackled Ethereum’s most common challenges, including limited scalability, issues with its consensus algorithm and excessive energy requirements. The biggest change was that it moved Ethereum from a Proof of Work (PoW) to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Ethereum 2.0 was rolled out over multiple phases, with Phase Two concluding in April 2023.
As increasing numbers of users are engaging with the Ethereum network, it has started facing obstacles that need to be overcome to ensure a viable future. These challenges include limited scalability, the limitations and the consequences of the proof of work consensus algorithm, such as the network’s vast energy requirements. Ether is one of the most popular altcoins and ERC20 tokens are the most popular tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum 2.0 is an update to the current Ethereum network that is set to address various issues for enhancing the ecosystem.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereWhat is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0 refers to a set of updates that aimed to resolve issues surrounding limited scalability, speed, and the limitations of the Proof of Work consensus mechanism of the Ethereum network. The core ideas around Ethereum 2.0 originated from Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum, and researcher Vlad Zamfir around the time of the Ethereum network’s creation.
Ethereum 2.0 was not a one-and-done update. Instead, it was rolled out in phases, with the gradual application of new features over two years to ensure a smooth transition from the existing ecosystem to the updated network.
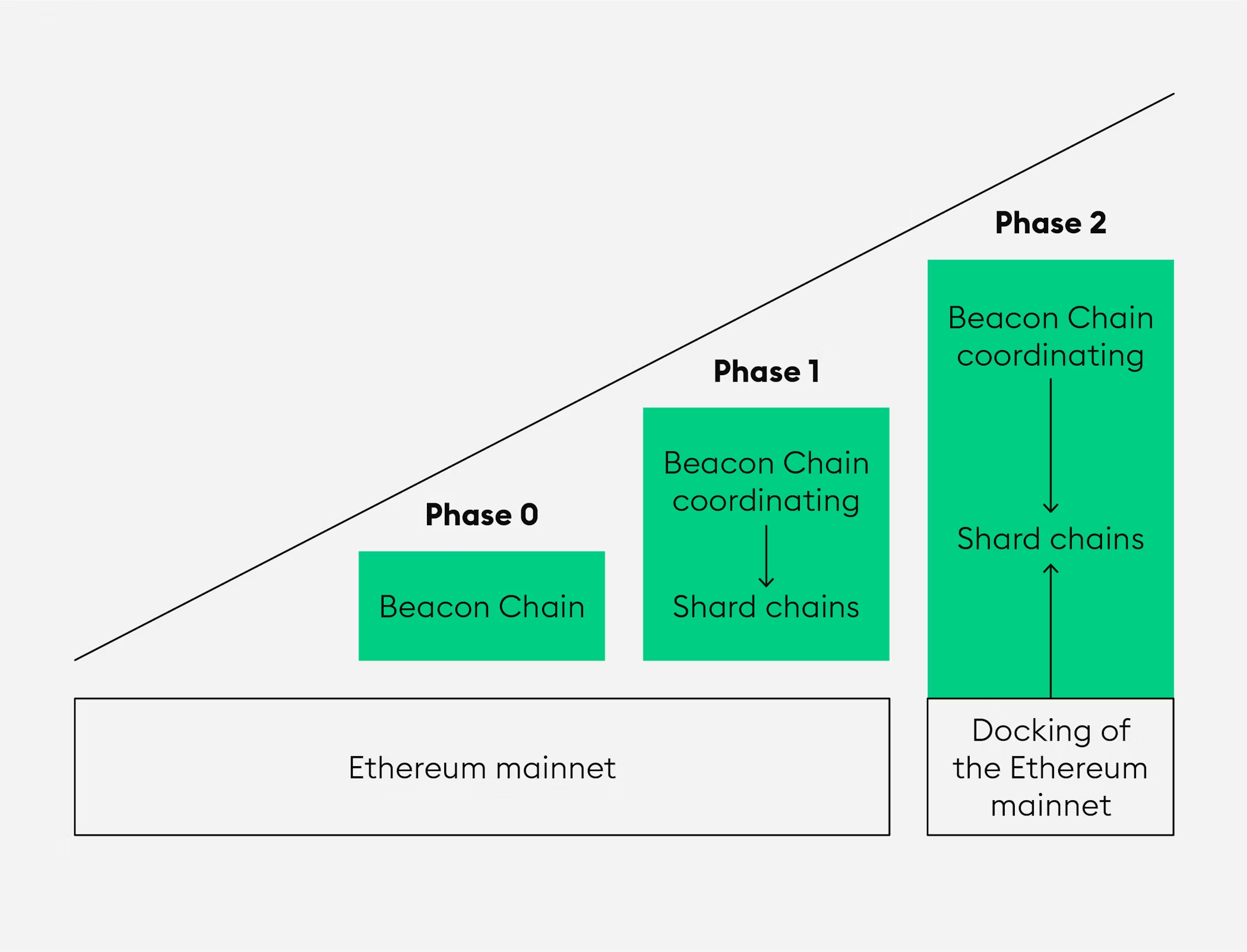
The process included three major milestones that rolled out from 2020 to 2023:
Phase 0: The launch of the Beacon Chain, which ran parallel to the Ethereum mainnet for two years.
Phase 1: Introduction of the shard chains, which gradually increased data availability and decreased transaction processing time.
Phase 2: Completion of the Merge, in which the Beacon Chain and the Ethereum mainnet combined into one.
Phase 0: The launch of the Beacon Chain
Launched on 1 December 2020, the Beacon Chain was conceived to run in parallel to the main Ethereum blockchain. As the first element of Ethereum 2.0, this launch is sometimes referred to as Phase 0.
The Beacon Chain was the coordinating mechanism behind the new Ethereum ecosystem, and was essential in introducing Proof-of-Stake to the Ethereum ecosystem. This means that since the launch of the Beacon Chain, users of the Ethereum network were able to stake ETH (however they weren’t able to withdraw their staked ETH until the completion of Phase 2 in April 2023). The Beacon Chain was also the coordinating entity of the 64 shards that were introduced during the shard chains phase.
It is important to note that the Beacon Chain did not change anything on the Ethereum mainnet. Up until the Merge of the two chains in Phase 2, they ran parallel to each other and functioned separately.
Phase 1: The Shard Chains
After the launch of the Beacon Chain in Phase 0 came Phase 1, during which the Ethereum ecosystem gradually shifted from running everything on a single main blockchain to distributing its load across 64 shards. A shard is a separate blockchain in an ecosystem that is connected to the main blockchain and other shards within the same ecosystem.
The shards communicate and transfer data between one another while securing the ecosystem and the shards run according to the algorithm. This allows for faster validation of transactions as validators only need to focus on a single, relatively-compact shard (one of the 64 that was assigned to them), instead of dealing with one substantial blockchain.
In Phase 1, the Ethereum network was already becoming faster and more scalable as more transactions could be processed. Additionally, hardware requirements dropped significantly for validators as each validator only stored the data for its respective shard. In the future, these changes may even enable running Ethereum on a mobile phone or laptop.
Phase 2: The Merge
September 2022 saw the completion of Phase 2, also known as the Merge. During this event, the Ethereum mainnet chain merged with the Beacon Chain that was launched in Phase 0, thereby completing the Ethereum 2.0 update.
During the Merge, the Proof of Work algorithm was entirely eliminated from the Ethereum ecosystem and Proof of Stake took full effect throughout the entire network. After merging, the Mainnet enabled the running of smart contracts in the renewed Ethereum ecosystem, so that Ethereum was once again running smoothly on a single blockchain.
Although the Merge saw the transition to Proof of Stake, it wasn’t until the Shanghai Upgrade in April 2023 that stakers on the Ethereum network were able to withdraw their staked funds. This mini-update was the last step in completing the full transition to Proof of Stake.
Main features of Ethereum 2.0
Increased scalability
Before Ethereum 2.0, the Ethereum network relied on the Ethereum mainnet, which had a limited number of transactions it was able to process - between 15 and 45 per second. Expanding to 64 shards decreased the time needed for validation of transactions, thereby improving not only the volume of transactions that can be processed, but also the speed of processing.
More sustainable
Before the Merge, Ethereum was using a Proof of Work consensus mechanism, which has several vulnerabilities. One remote possibility is that of a 51% attack, which is when a miner or a group of miners takes a majority control of the network and uses the control to double-spend the currency. Although unlikely, it is still a real risk. For instance, Ethereum Classic, a fork of Ethereum that still runs on Proof of Work, has repeatedly fallen victim to 51% attacks.
But one of the largest issues of Proof of Work is its unsustainable computing power. PoW uses up vast amounts of electricity in order to validate transactions and create new blocks. Proof of Stake eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining because the network is secured by validators who stake ETH to validate transactions, which doesn’t consume nearly as much energy as PoW. PoS is therefore considered to be more environmentally friendly than PoW, making Ethereum a more eco-friendly platform post-Merge. It’s estimated that Ethereum’s energy consumption will be reduced by around 99.95% with PoS.
Staking on the updated network
With the introduction of the Beacon Chain and the move to PoS, users of the Ethereum network are now able to stake ETH and to earn rewards for staking and keeping the network safe. The more ETH a validator stakes, the better their chances are of getting a validation task to receive rewards. By staking sufficient ETH, anyone can become a validator without needing top-performance computing power. As of April 2023, stakers are able to withdraw their staked funds and rewards.
The PoS algorithm also protects the network from the possibility of coordinated attacks that could arise from one agent controlling 51% or more of the networks’ overall computing power. With the PoS algorithm, if a validator were to act unlawfully and attempt to attack a shard, the algorithm could automatically destroy their stake. Therefore, this penalty system is intended to disincentivise any coordinated attack. Validators are randomly assigned to and distributed among the shards to greatly reduce the chance of a planned and concentrated attack against a single shard.
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any digital assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in digital assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.