What is SegWit (Segregated Witness) and how does it work?
SegWit was an update to the Bitcoin protocol and stands for “segregated witness consensus layer”, a technological feature created to optimise transactions in 2015.
SegWit is a change in Bitcoin’s protocol
SegWit was pushed through in a soft fork of the original Bitcoin network after the Bitcoin scalability debate reached its peak in late 2017
Bitcoin Cash is arguably the main competitor supported by the other fraction
Presently, SegWit is a scaling solution used by several different cryptocurrency networks including Litecoin
In this article, you’ll learn what SegWit is and why it matters for the future of the Bitcoin network.
Bitcoin and Scalability
While the Bitcoin network has been operating without any notable incidents for more than 10 years now, there were multiple occasions where transaction costs reached high amounts that were no longer feasible. Consequently, Bitcoin developers were debating how best to scale the network to handle growing transaction volumes in the future.
In 2017, this debate came to a head with a split in the Bitcoin development community between implementing a feature called SegWit with a soft fork.
What is SegWit?
The main purpose of SegWit is to improve transaction throughput on a blockchain network. It is worth noting that the first cryptocurrency to implement the SegWit layer was not Bitcoin, but Litecoin.
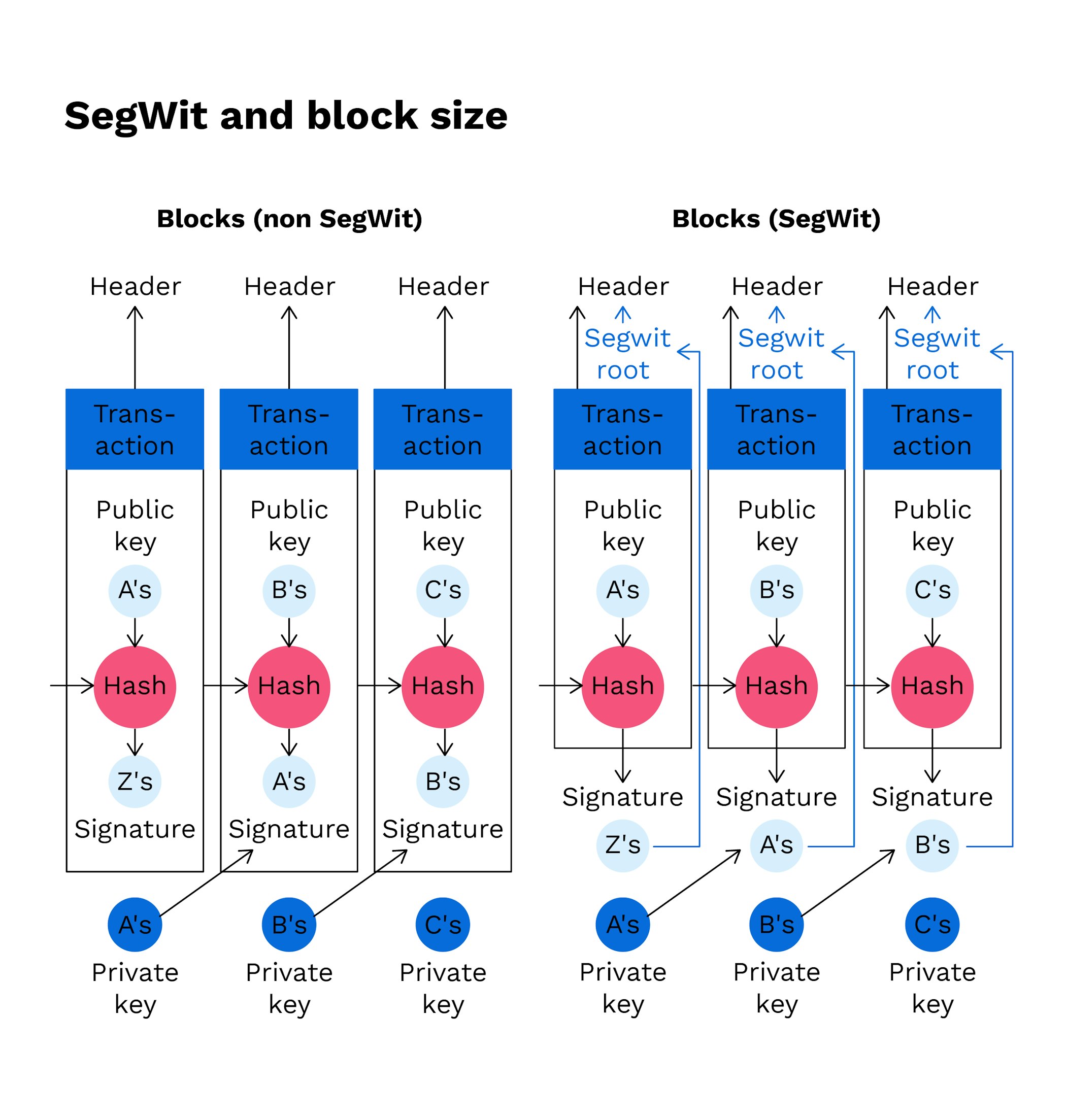
In essence, SegWit reduces the weight of transactions in a block on the blockchain by segregating a transaction into two sections; effectively increasing the amount of transactions one can include in a block of the same size.
The first part of a transaction contains the wallet addresses of the sender and receiver and the second part contains the “witness data” containing transaction signatures. SegWit removes the “witness data” from the main block, therefore notably reducing transaction size. The transactions consequently require less space, enabling more transactions per block and greatly increasing the capacity of the Bitcoin network.
The first part of a transaction contains the wallet addresses of the sender and receiver and the second part contains the “witness data” containing transaction signatures.
Further, SegWit provided the fix to a flaw in the Bitcoin protocol which let users change transaction hashes of transactions. The change of just one character in a digital signature results in an entirely different transaction hash. As the signature is moved out of the transaction data into the segregated witness data, it is no longer possible to change the transaction ID. Consequently, SegWit is a solution to transaction malleability.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereWhat are the advantages of SegWit?
SegWit is a feature of the Bitcoin protocol that has now been adopted by most Bitcoin-based services. Users of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency exchanges can easily verify with a quick Google search, that the exchange they are using supports SegWit transactions. However, SegWit’s benefit to Bitcoin goes beyond simply making blocks smaller and making the network faster.
SegWit stands as the first step towards scalability for Bitcoin and several other major cryptocurrency networks. For the Bitcoin network to function, quick and efficient blockchain networks are a prerequisite and SegWit paved the way towards scaling blockchain networks for widespread adoption, both directly and indirectly.
What are the downsides of SegWit?
Despite the fact that SegWit transaction adoption in the Bitcoin network is increasing and reached an all-time high of more than 65% at the beginning of 2020, possible adaptations of the Bitcoin network take a much longer time than those in altcoin networks, owing to the sheer significance and size of Bitcoin - there is too much at stake. On another note, not everyone supports SegWit transactions, even now.
The continuous scaling debate has likely been the main reason behind several hard forks off the Bitcoin blockchain over the last few years. The most prominent of these forks was the Bitcoin Cash hard fork, which took place on 1 August 2017. Bitcoin Cash forked again on 15 November 2018 and increased the network’s block size limit from 1MB to 8MB.
Moving forward, it will be interesting to see which type of scaling solution will be the most widely adopted amongst cryptocurrencies in the long term.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowDISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.