What is a market maker?
Market makers are employed to ensure sufficient liquidity and efficient trading on financial markets.
For a market to count as an attractive environment for trading, substantial supply and demand for the respective asset and a high level of trading activity are needed to ensure that orders are filled quickly.
High liquidity is associated with favorable market conditions and lower risk.
Market makers provide offer prices and bid prices for trading pairs and act as a buyer or seller for a transaction in the absence of a suitable counterparty.
In this article, you will find out about market makers and their role.
Maker orders
On a cryptocurrency exchange, orders are either charged with “maker fees” or “taker fees”.
An order which is adding liquidity to the order book until another crypto trader picks it up helps to “make the market”. As liquidity on an exchange indicates interest in a market based on trading volume and active traders, crypto trading fees for “maker orders” are often lower than other fees because they incentivise traders.
To be deemed a maker order, the would-be maker needs to place a buy order lower in price than the lowest sell order, or a sell order that is higher in price than the highest buy order needs to be placed by the trader. The drawback of being in a maker role is that it may take some time until the set price is triggered and the order is filled.
Taker orders
“Takers”, on the other hand, are the counterpart of “makers”. Takers “take liquidity” out of order books. They look for orders they can immediately fill. Such an order could be a market order: an instant purchase or sale of a cryptocurrency for the best price available at this time. A market order will always immediately fill or be fully rejected if at that point in time there is not sufficient liquidity in an order book.
Finally, don’t forget that “makers” and “takers” are fees that are applied while a “market maker” is a type of entity that promotes liquidity in a market. Let’s look at the role of a market maker in more detail.
Why is there a need for a market maker?
Market maker services are often provided by large financial institutions due to required volumes, however, in some instances, also by individual traders. However, while each crypto trader is a market participant with a share in its operating volume, the prerequisites for providing the necessary trading volumes are so stringent that only specialised institutions offering market making as their core service institutions can meet them in comparison to a regular trader. Consequently, parties that are interested in providing services as market makers need to prove that they are authorised, possess impeccable credit ratings and are able to meet a broad range of other obligations which vary according to global region.
To ensure that there are no conflicts of interest, crypto traders trading on a crypto exchange should conduct their due diligence and verify that the exchange and the market maker are two distinctly separate entities.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereWhy are market makers needed?
While a crypto exchange provides the infrastructure to facilitate the sale or purchase of an asset for traders looking to buy or to sell, market makers provide liquidity in cryptocurrency markets and thus ensure sufficient liquidity in the order books. In short, a market maker acts as an intermediary/broker between supply and demand for securities.
This way, traders are able to liquidate their positions smoothly and at short notice. Let’s say you want to sell an asset with a traditionally low liquidity on a crypto exchange - you will be able to do so thanks to the market maker.
Another reason why market makers are needed is that they ensure price continuity on a market with a relatively narrow bid-ask spread, which we will get to in a moment. A market characterised by strong price continuity is not only considered reliable and trustworthy by crypto traders, it is also a sign for strong liquidity with many participants making transactions, resulting in greater profit for the market maker. If the rule of price continuity is not observed, market makers tend to make losses.
How do market makers make money?
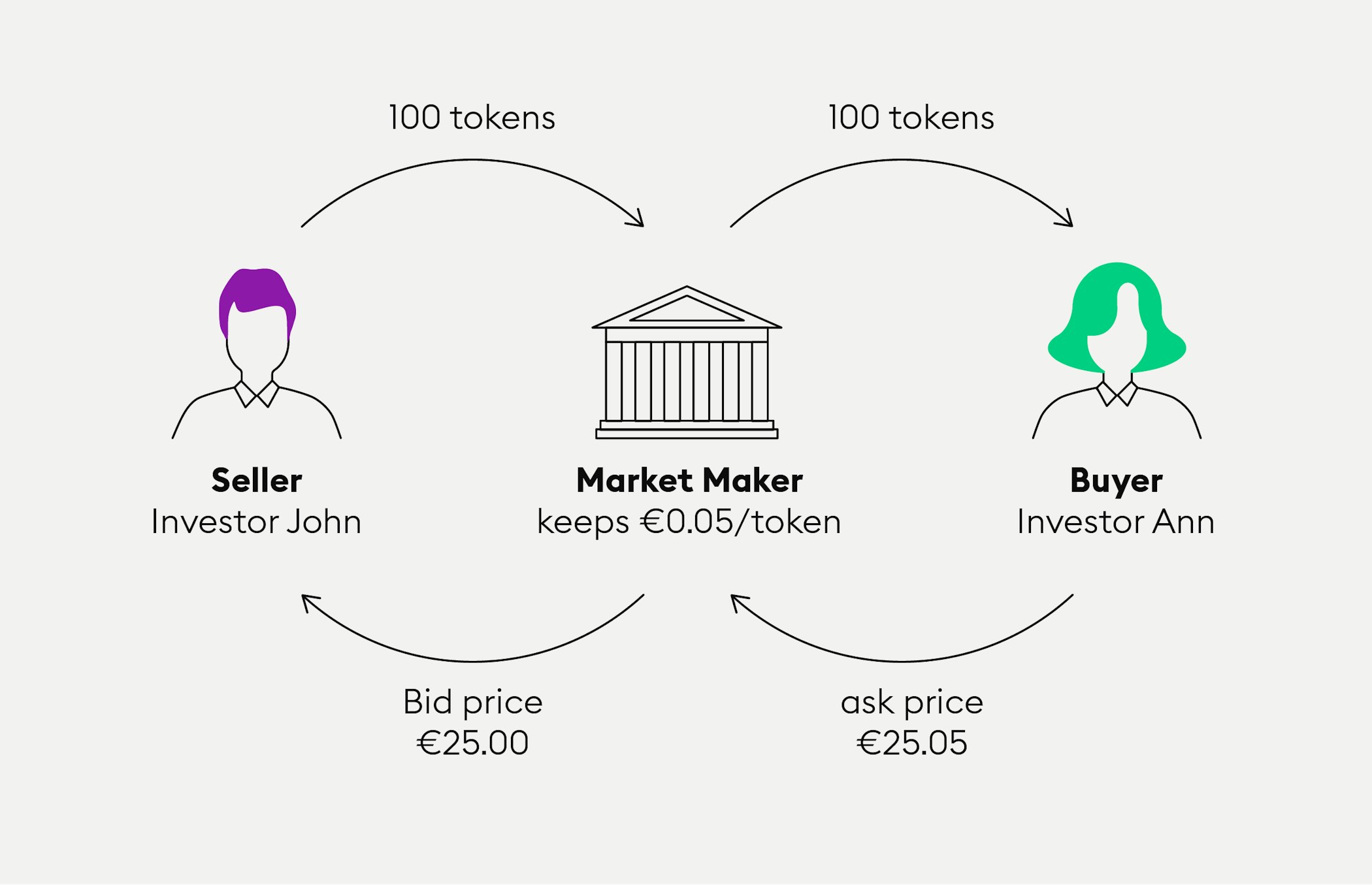
For providing their services to crypto traders, market makers charge a spread on the buying and selling price. Now remember the market maker acting as a buyer or seller puts up ask prices and bid prices and traders buy and sell at those prices.
Unlike crypto traders, market makers do not make money by buying low or selling high but through spreads. The term “spread” here means the difference between the bid price at which traders are selling and the slightly lower actual price, while traders wanting to buy are charged the ask price, which is slightly higher than the market price. The spread between the price traders receive and the market price is the market maker's profit. Typically market makers also charge crypto exchanges a general fee for their services. Our infographic illustrates how the market maker makes its money with spreads.
Why is the spread important?
The bid-ask spread illustrates the difference between the offered buyer price and the offered seller price. The higher the number of traders and market makers in a market, the stronger the competition and the more narrow the spreads. A narrow bid-ask spread is favourable because if spreads are too high, the chances of successful transactions are greatly diminished. This can happen, for example, if demand in the market is much higher than supply.
What do market maker services involve?
Market makers should be neutral and set their offers according to demand and supply in a securities market. High supply paired with low demand will be reflected in a low ask or bid price and low supply for an in high demand will result in a high ask or bid price. Therefore, market makers place buy and sell orders on a large scale, reflecting the supply and demand of a particular market.
When providing quotes for buying and selling assets, a reliable market maker will provide a range of prices, regardless of the level of volatility. In order to facilitate high-frequency trading, market makers need to ensure that they, as a partner, are available to accept a deal at the provided rate and have the asset available for trading near immediately once an order is placed. Finally, they need to execute the transaction at the market rate.
DISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.