How does a blockchain work?
The internet promised an age of decentralised freedom, but today we still heavily rely on centralised players like we did in the analogue age. Many of the processes that run our global financial system and the world at large, are still paper-based and at risk of human error from centralised authorities. Blockchain technology is here to change that.
A blockchain is a decentralised, tamper-proof database
A blockchain is an ingenious system for ensuring mutual trust and collective consensus
A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin is just one of a blockchain’s many applications
Contracts, digital identities, logistics, just about every kind of asset and so much more can also benefit from utilising a blockchain
In this article, you will learn blockchain fundamentals.
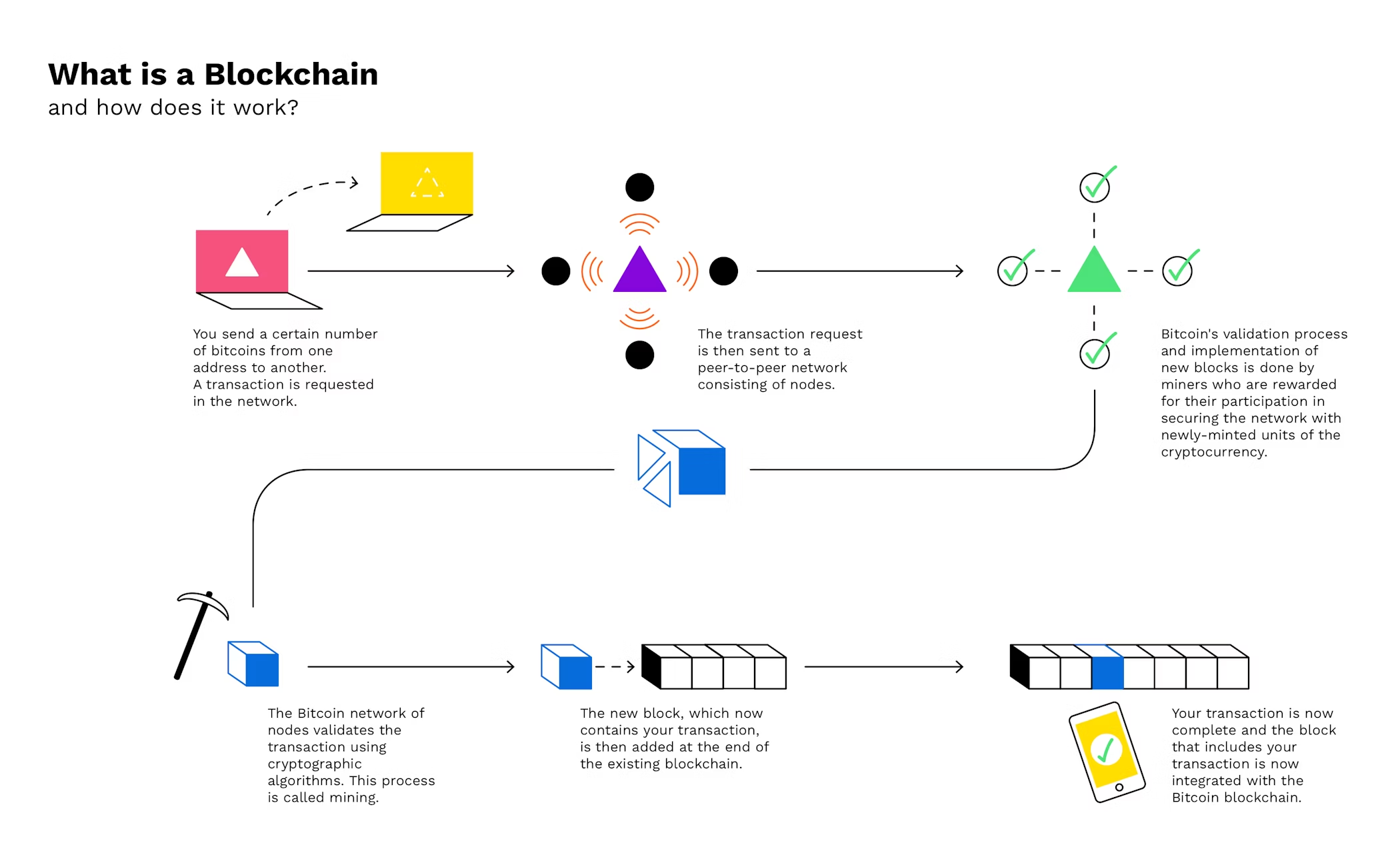
What is a blockchain?
A blockchain is a special type of database. Transactions are not governed by a single party, but rather the entire transaction history is recorded in a decentralised, distributed ledger.
Blockchain technology is safe and robust and thus ideal for storing and processing sensitive information. The revolutionary aspect behind blockchain is that processes are not completed by one, but by many computers, simultaneously.
Bitcoin is a typical application. Trust in Bitcoin is secured through a decentralised, immutable ledger that is not run by a single company or government but by an independent community of computers all around the world.
All computers are in the same network, called a peer-to-peer network. Inside the industry, this model is often called a “distributed trust model”.
New to Bitpanda? Get started today!
Sign up hereA model of trust
Blockchains offer groundbreaking technology with the potential to change the internet and even the world for many reasons. As we dive deeper into how blockchains work, you will find it increasingly easy to understand exactly why.
Each node contains a complete image of a blockchain’s network.
Who can be trusted in a digital space, where everything can easily be copied and most users are anonymous? Blockchain can help to solve this pressing question.
A blockchain is not updated and validated by a single individual, but by hundreds, thousands, or even millions of community members in regular timeframes.
Instead of one central party such as a company, government or bank, the entire blockchain network agrees on a shared “reality”, i.e. complete history of every transaction that has ever taken place within the network. This agreement is called consensus.
Because every single transaction that has ever taken place within the network is recorded and permanently stored, it is not possible to change the ledger’s history or send the same transaction twice (i.e. double spend).
This certainty creates mutual trust.
In other words, participants of a blockchain network don’t even have to trust each other because no single user can cheat the system as a whole.
Blockchain technology is suitable for transactions between parties that need to be verifiable and permanent, such as contracts, ownership of intellectual property, identification, and, of course, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
How do blockchains work?
To ensure that the network’s transaction history is not manipulated by anyone, the community behind the network has to agree on a common “reality”.
In a blockchain, transactions are stored in blocks, with each newly generated block referring to the block before it with a unique identifying number called a “hash.” These blocks constitute a chain, hence the name “blockchain”. This chain continues on indefinitely.
In the case of blockchains such as Bitcoin, trust is based on technological features such as the fact that all blocks can be viewed by the public. No transaction is added to a block without first being verified by a miner - a special type of computer in the network. This way the community ensures that no fraudulent transaction is recorded in a blockchain.
Consequently, a blockchain can even be used by parties who don’t necessarily trust each other to do business because they know their transactions are tamper-proof.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowDISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.