The problem of scalability in the Bitcoin network
One of the present drawbacks of using the Bitcoin network for payment transactions is the issue of network scalability.
When transactions are verified in the Bitcoin network, in theory each node in the decentralised system has to verify every transaction
The Bitcoin network can only process a certain number of transactions in a set time frame, such as per block
In its most basic definition, scalability is the capability of the network to handle a growing amount of transactions
In a more detailed context, scalability factors include throughput, transaction times, latency, and security
In this article, you are going to learn about the issue of scalability in blockchain technology.
Verification of transactions
Transactions in the Bitcoin network are verified in a process called mining. The computers of miners collect transactions that have been dispatched into blocks. The nodes then compete to be the first node to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle. The objective is to be the first miner to validate the new block. A block is only accepted into the blockchain if all transactions in this block are valid and have not already been spent.
As Satoshi Nakamoto estimates in his whitepaper on Bitcoin, blocks are generated just about every ten minutes - this is known as the “block time” of the Bitcoin network. It is the estimated length of time it takes to mine a block. A block is usually about 1MB in size. If it takes longer to mine a block in the Bitcoin network, the “difficulty” level will be reduced, if it takes less time, the difficulty is increased. The difficulty adjustment takes place roughly every 2016 blocks (about every two weeks).
Transaction volumes
Presently, total value being moved in the Bitcoin network is increasing on a yearly basis, as is the number of processed transactions. As each transaction has to be at least 250 bytes - a figure that is hard-coded into the Bitcoin protocol - the Bitcoin network can process up to 7 transactions per second (tps) if the block time is ten minutes. Ethereum processes about 15 tps and Ripple is the fastest, with a capacity to process about 1,500 tps.
Presently, total value being moved in the Bitcoin network is increasing on a yearly basis, as is the number of processed transactions.
Why is scalability an issue?
In order to support the adoption rate of cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions, to begin with, a network needs to demonstrate its capability to handle a certain amount of transactions without processing issues and delays beyond doubt. Secondly, the network needs to provide credibility that it will be able to handle a growing amount of transactions in the future. This is what “to scale up” a network means - to increase in size, capacity and consequently, in security. On the other hand, a network needs to provide sufficient incentives to miners in terms of transaction fees to keep them engaged and competitive.
Compared to traditional payment providers such as VISA or PayPal, the transaction capacities of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are very low. The world’s leader in digital payments, VISA, claims that it is able to handle more than 65,000 transaction messages a second and actually handles an average of 150 million transactions every day. In contrast, the payment network PayPal “only” handles 193 transactions per second, or about 5 million transactions a day.
Therefore, network speed and security are the two prevailing factors that determine the reputation of a payment network. Consequently, the present infrastructure of cryptocurrency networks will need to be expanded in a suitable way to absorb increasing transaction volumes along with an increasing number of users.
The question of scaling solutions
The Bitcoin community activated SegWit in 2017 as a soft fork to the Bitcoin protocol to enable second-layer solutions for scaling. In essence, SegWit basically involved removing (segregating) the “witness” - data needed to check the validity of transactions - from the list of inputs.
Another scaling solution that aims to reduce the amount of data in the blockchain is the Lightning Network, a "Layer 2" payment protocol operating on top of Bitcoin based on a network of bidirectional payment channels, thus facilitating everyday transactions without charging unreasonable fees.
After Bitcoin transactions had approached network limits in late 2017, two basic schools of thought on network scaling emerged. Supporters of one group wanted to focus on increasing the limit of block size, the other focusing on off-chain scaling by adding additional protocols on higher layers, somewhat similar to the present structure of the internet.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
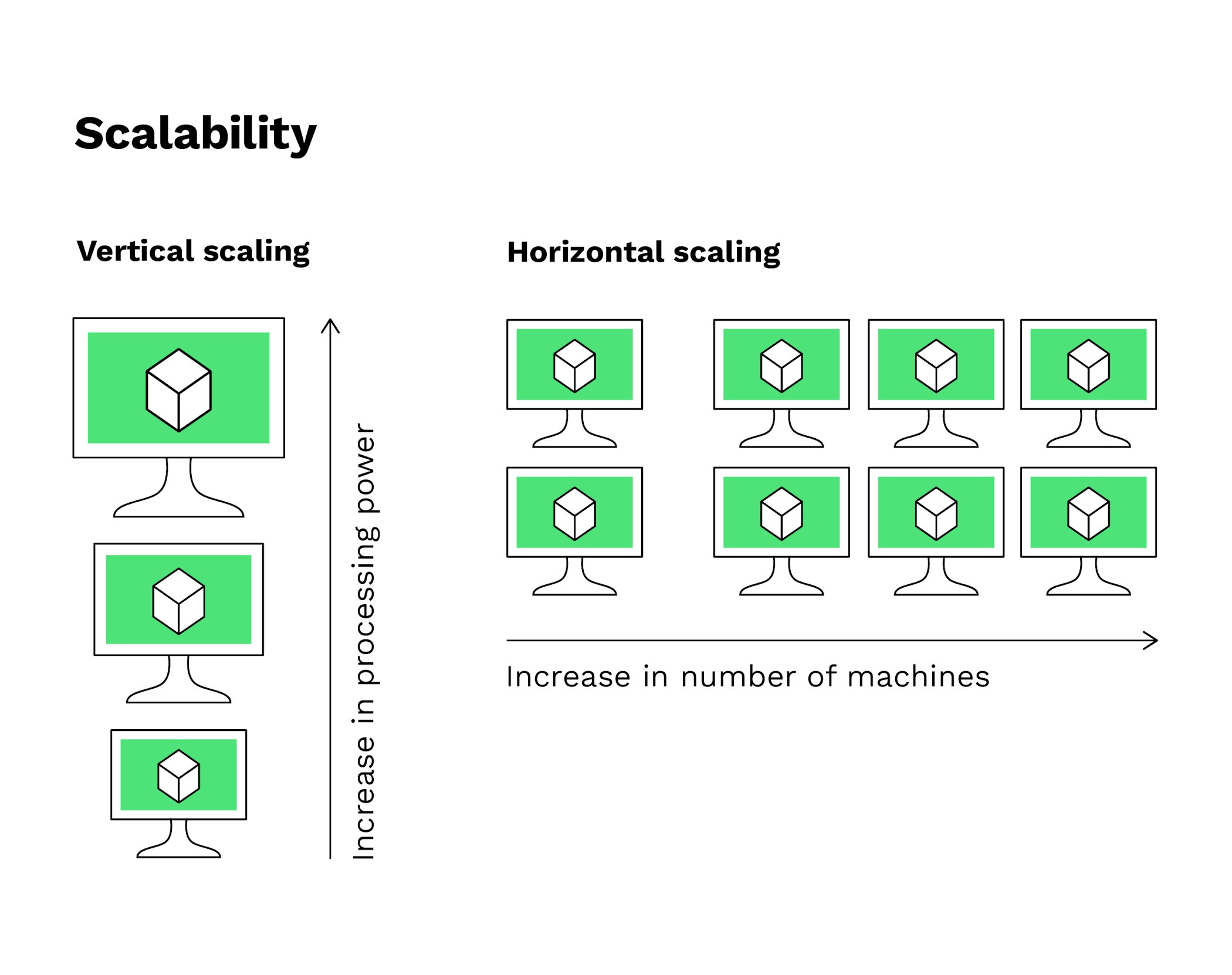
Sign up hereHorizontal and vertical scaling
A further feature to bear in mind regarding the effectiveness of scaling solutions is a division into what are known as horizontal and vertical scaling solutions. Both have advantages and disadvantages regarding decentralisation.
Vertical scaling involves adding processing power and memory to each node, thus creating more powerful nodes. Consequently, the efficiency of individual transactions is improved. Horizontal scaling, on the other hand, entails adding more machines to a system and improving overall throughput capacity. In summary, fewer nodes and thus higher centralisation of a network (such as EOS) generally increase network speed, while transparency and overall immutability are lower than in a highly decentralised network such as Bitcoin.
It is currently unlikely that, in terms of technology, one single scaling solution will manage to take into consideration all factors to provide the optimal solution for the Bitcoin network. However, many other coins have proposals they are working on to provide different solutions to this predicament as technology is making headway.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowDISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.