What is the purpose of the Lightning Network for Bitcoin?
In response to Bitcoin network scaling issues, the Lightning Network was one of the proposed solutions along with SegWit.
Limitations of the Bitcoin network’s capacity to process transactions led to a block size debate early on
The Lightning Network evolved into a scaling solution outside the main Bitcoin network, lowering transaction fees and speeding up transaction processes
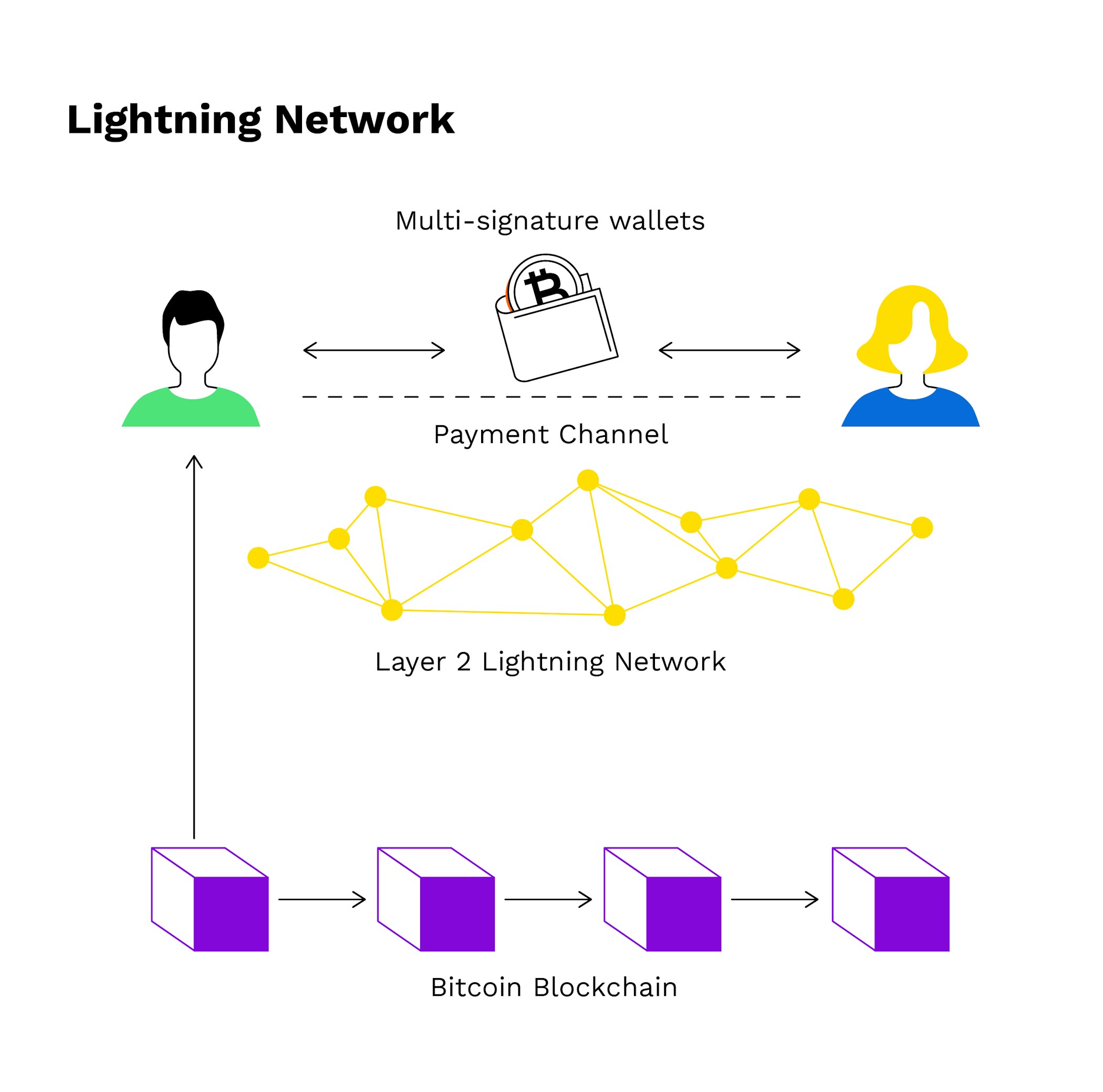
The Lightning Network is a web-shaped network of made up of underlying payment channels as core elements in a second layer
The main selling points for the Lightning Network are instant payments, scalability and low fees
The number of users participating increases its usability as it is more likely a payment channel is available
In this article, you will learn everything about the Lightning Network.
In response to Bitcoin network scaling issues, the Lightning Network was one of the proposed solutions along with SegWit and increasing block size, the solution that ultimately became Bitcoin Cash. In fact, despite SegWit being adopted much quicker, the Lightning Network was proposed first. Like Bitcoin nodes, payment channels act as gateways to the Lightning Network but unlike Bitcoin, there are no miners. Instead, the Lightning Network is kept secure through its own smart contracts.
A web of payment channels
The core element of the Lightning Network is a payment channel. To participate in the network, you need special software - a Lightning Network client - that takes care of facilitating users’ payments through creating payment channels.
For example, using a payment channel, two users in the Bitcoin network are able to send transactions and consequently update the balance of the channel up to a limit that has been locked in the payment channel beforehand.
After an initial transaction for funding has been made to open a channel in the Lightning Network, the users themselves can make any number of transactions with one another without these transactions being stored in the blockchain, consequently relieving the burden on the blockchain and scaling up the network in the process.
How does the Lightning Network support Bitcoin?
After each payment, the current balance is recorded in a “commitment transaction” that has to be signed off by both parties. This idea is based on a concept similar to that of a current account in classic commercial law, where periodic billing has been agreed upon as part of a permanent business relationship and mutual services are continually booked.
After each payment, the current balance is recorded in a “commitment transaction” that has to be signed off by both parties.
However, in the case of a payment channel in the Lightning Network, claims are only settled once one of the participants closes the payment channel by publishing a settlement transaction. It is this action that records the final balance between both parties in the final commitment transaction directly on the blockchain. Unlike in the case of a current account, the two parties involved do not need to trust each other. Still, transactions in a payment channel only take place upon mutual agreement of both parties. The throughput of the payment channel is only limited by latency and the throughput of the TCP socket used.
It is worth mentioning here that users should still pay attention to blockchain activity in regards to settling these transactions. It is possible that a user would try to settle an account with an out-of-date settlement transaction. The other party should, in this case, publish the later transaction settlement in order to dispute it.
Channels are the paths from one cryptocurrency wallet to another. In order to use the Lightning Network, users have to get a cryptocurrency wallet that supports the Lightning Network.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereHow do Bitcoin users benefit from the Lightning Network?
Lightning fees are much lower than Bitcoin’s and transactions are finished faster
It is not just Bitcoin’s block time that needs to be addressed before we can have that elusive cup of Bitcoin coffee. Transaction fees also need to be as low as possible, while keeping miners on the network, which is a delicate balance to maintain. Anytime a user carries out more than one transaction on the Lightning Network, the fees will be lower than the Bitcoin network fees.
Beyond payment channels in the network, there are also people running payment nodes, which charge fees to make sure payments get to where they need to go. These payment nodes are akin to transfer services like Transferwise. Their role is to find the quickest path for each payment and to keep all payments secure (alongside Lightning’s smart contracts).
This has already led to a jump ahead of Bitcoin’s average of 7-10 transactions per second. The trouble is in saying just how much that jump is as of now, since Lightning’s transaction speed is determined by how much Bitcoin has been allocated towards opening a channel.
Picture a secured credit card. If you only allotted $1,000 to it, then that is the maximum you can use at any time. So, while Lightning’s overall maximum transactions per second might be very high, it is more accurate to measure its capacity on a channel-by-channel basis. Since Lightning’s average channel capacity is just over $200 and the average fee per transaction is well under $0.01, it could already be well on its way to being the crypto network for everyday purchases.
What are the downsides of the Lightning Network?
It needs to become even easier for the average person to use
Despite the surrounding hype, the Lightning Network has not quite reached its goal of making everyday payments viable. The average person cannot access it without the help of third-party wallet providers and payment facilitators. These third-parties, in turn, take fees for providing the services they provide. Essentially, the Lightning Network has not really made Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrencies more user-friendly.
Payment nodes are a double-edged sword
Payment nodes both assist users and complicate the process of scaling the Lightning Network at the same time. On the one hand, they do make it simpler for the average person to join by partnering with widely-used wallet providers and thus eliminating the friction of understanding the technicalities of payment channels. On the other hand, they make it more difficult for people who are new to the Lightning Network to get on board. Essentially, there is an extra step between peers in a peer-to-peer network.
Similarly to miners, payment nodes are like businesses that rely on fees to exist. Therefore, it may only be a matter of time before they begin to prefer processing those transactions that have paid higher fees to those with smaller amounts, which would go against the vision of working on Bitcoin adoption in daily life. It will be interesting to see how the Bitcoin community will address these issues.
Are you ready to buy cryptocurrencies?
Get started nowDISCLAIMER
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any crypto assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in crypto assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.