How to start staking crypto
Crypto holders can contribute to the security of a proof of stake network by staking their crypto coins and tokens. In return, they receive rewards in the form of the staked cryptocurrency.
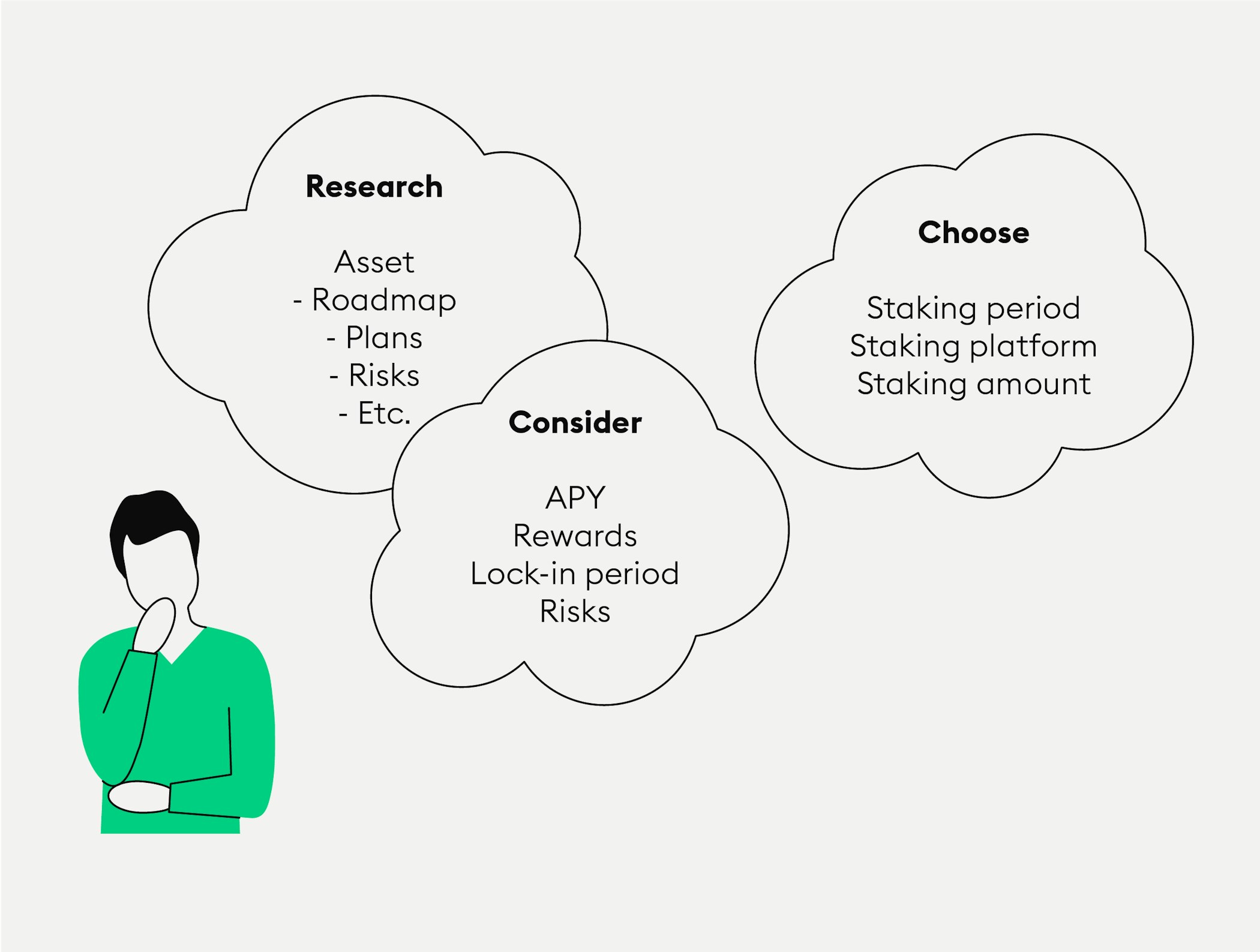
In this guide, we explain how you can stake your crypto coins and tokens profitably. We outline how to select a suitable platform, choose a stakeable asset, and carry out staking. With this method, you can delegate your coins and tokens today, and build a passive income through attractive rewards.
Crypto staking offers an attractive opportunity to generate passive returns in the form of staking rewards. Before you begin, it’s important to thoroughly understand what staking is, the risks involved, and the concept of a staking pool. Only when you have a significant grasp of the basics of staking and understand how validators contribute to the security of a proof of stake network can you make an informed decision about your own staking strategy.
Which cryptocurrencies can be staked?
In recent years, numerous staking projects have been established, including networks like Tron (TRX), Tezos (XTZ), Cosmos (ATOM), The Graph (GRT), Kusama (KSM), Polygon (POL), Near Protocol (NEAR), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), and Polkadot (DOT). Staking Ethereum (ETH) has also become possible with Ethereum 2.0 on a proof of stake basis.
Tron (TRX)
TRON was initially founded as a smart contract platform to enhance the Ethereum network but later moved to its own blockchain to create a developer-friendly ecosystem for decentralised applications (DApps). The TRON network operates on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPos) system, and transactions can be supported by staking the native TRX token.
Tezos (XTZ)
Tezos is a self-amending, permissionless open-source protocol that enables the development of other projects and meta upgrades. Tezos is based on the proof of stake consensus and allows its community to participate in governance as “Bakers” and stake the native network token XTZ.
Solana (SOL)
Solana claims to be the fastest blockchain in the world, based on a single layer without splitting the network into different layers during the scaling process. Holders of Solana’s native cryptocurrency, SOL, can delegate tokens to network validators for staking, thus contributing to transaction verification and new block creation.
Cosmos (ATOM)
Cosmos, also known as the “Internet of Blockchains,” is built on a multi-chain framework that connects various blockchains within the same protocol to facilitate scalability and interoperability between assets. Cosmos operates on a proof of stake consensus mechanism running on an engine called “Tendermint.” Governance and staking in the network are managed through the native token ATOM.
The Graph (GRT)
The Graph provides an indexing protocol to enable queries in networks like Ethereum. All Ethereum data can be searched through simple queries, promoting blockchain data accessibility and facilitating DApp development. The Graph network services are provided by the community, divided into indexers, curators, and delegators. GRT is the native ERC20 token of The Graph, used as a medium of exchange and for paying rewards.
Kusama (KSM)
Kusama is a platform for developers who want to quickly implement blockchain-based projects, enabled by its lower security and governance requirements. This allows for rapid testing and implementation of new features, accelerating the development of new applications. Kusama’s native coin is used for staking and governance in the Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism. Validators are assigned stakes on the Kusama blockchain, earning a share of the rewards.
Polygon (POL)
The Polygon network was built “by developers for developers” to enhance the scalability and accessibility of Ethereum by operating sidechains connected to the Ethereum mainnet. Data is collected in proof of stake checkpoints or groups on a sidechain. Polygon’s native token POL is used for network operations and crypto staking.
Near Protocol (NEAR)
Near Protocol aims to develop smooth operations for the next generation of DApps and is the world’s first climate-neutral blockchain. It’s a sharded Layer-1 and proof of stake network that aims for fully decentralised and linear scaling across millions of nodes. The native token, NEAR, is used by token holders for delegated crypto staking, ensuring network security and allowing users to earn rewards through validator-operated staking pools.
Cardano (ADA)
The Cardano network aims to tackle issues like scalability, security, and the social and economic integration of blockchains. All developments behind the Cardano network are based on scientific approaches and are continuously and methodically improved. Research and findings are subject to strict standards and are reviewed by various independent bodies.
The network runs on a proof of stake consensus algorithm called “Ouroboros.” Cardano staking, operated through staking pools, is so popular that many automatically think of Cardano’s native token ADA when referring to crypto staking.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot offers a heterogeneous multichain where various data structures can be hosted. This means that different blockchains, known as parachains, can be implemented on Polkadot, enabling them to communicate. The focus is on scalability, governance, and interoperability, as all information from individual parachains can be processed in parallel across different network areas.
Parachains can be used in various ways, such as for decentralised finance (DeFi) or non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Polkadot allows staking as it is based on a Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) system. Holders of the native token DOT can stake as validators or nominators in the network to generate additional income through rewards.
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum 2.0 is a comprehensive upgrade of the Ethereum network, addressing existing challenges like limited scalability, consensus algorithm issues, and high energy demand. The update significantly improves scalability by transitioning the blockchain from a proof of work to a proof of stake consensus mechanism. Transaction verification and block creation are no longer carried out by energy-intensive crypto mining but through staking. This not only reduces energy demand but also increases the security and efficiency of the network.
With the implementation of Ethereum 2.0, ETH staking is introduced. Validators can earn rewards by staking Ether (ETH) to validate transactions. With the phased transition to Ethereum 2.0, Ethereum has become a more powerful and eco-friendly blockchain network.
Where can you stake crypto coins and tokens?
You can stake coins and tokens with crypto brokers or exchanges, on staking or DeFi platforms, or directly in the blockchain network. While staking your coins in the blockchain network requires technical knowledge and access to your own validator node, crypto brokers offer easy and direct access to staking.
Staking pools also allow you to join other delegators (investors) to increase your chance of staking rewards. Depending on your technical expertise and willingness to engage in complex processes, different options are available to start crypto staking.
Crypto staking with brokers like Bitpanda
If you want to use a crypto broker service, Bitpanda Staking offers an ideal solution. You can stake your crypto coins and tokens with just one click and earn up to 25% APY. The rewards are paid out weekly, and your assets are not tied to cumbersome lock-in periods.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to crypto staking with Bitpanda:
Register with the crypto broker of your choice: Create your account with a valid email address and a secure password to start trading and staking cryptocurrencies.
Buy or transfer a stakeable cryptocurrency: Load a crypto coin or token for staking, such as Ethereum (ETH) or Solana (SOL).
Stake your crypto assets: Navigate to your purchased asset, choose the staking option, and actively participate in the transaction validation in the blockchain network.
Benefit from weekly rewards: Sit back and enjoy the weekly staking rewards.
New to Bitpanda? Register your account today!
Sign up hereStaking with crypto exchanges
Staking via crypto exchanges requires a deep understanding of crypto trading processes compared to crypto brokers. First, you should choose an exchange that supports staking with your chosen cryptocurrency. After creating an account, select the staking options and check which assets are available for staking e.g. Ethereum (ETH).
The next step involves setting up your wallet to manage the cryptocurrencies securely. Once your wallet is ready, you need to transfer the chosen cryptocurrency to it for staking. You can either transfer coins or tokens from an existing wallet or buy the cryptocurrency through the exchange. Before you start staking, familiarise yourself with the conditions and process to delegate the chosen cryptocurrency successfully.
Also, it’s important to understand that your staked assets might be subject to certain conditions like lock-in periods, depending on the exchange. Finally, make sure to consider the reward payout – it can be daily, weekly, or monthly, depending on the crypto exchange and staking option.
Stake with staking or DeFi platforms
Staking on staking or DeFi platforms varies greatly between different providers. Each platform has its own conditions and procedures, so there is no standardised approach to crypto staking.
First, you need to select a trustworthy and reliable staking or DeFi platform and create an account. Consider the offered cryptocurrencies, platform security standards, and potential returns. After registering, connect your crypto wallet to the platform. If you don’t have your own crypto wallet, you must create one first.
Before actual crypto staking, familiarise yourself with the specific processes on the platform. This usually involves selecting the cryptocurrency to stake and the amount. Each platform has its own policies on lock-in periods and minimum stakes, so it’s important to research thoroughly beforehand. The way rewards are paid out can also vary.
Overall, staking on staking or DeFi platforms requires an individual approach and thorough research to understand the specific processes and conditions of the chosen platform.
Staking directly in the crypto network
Staking directly in a blockchain network requires a good deal of technical understanding. First, you need to select a suitable network for staking, such as Ethereum (ETH) or Cardano (ADA). Each network has its own staking rules and requirements.
Once you have chosen a network, you should thoroughly research the specific staking requirements. These include the minimum staking amount, possible lock-in periods, reward mechanisms, and potential staking risks such as slashing. Next, set up a suitable crypto wallet for staking that is also supported by the chosen network.
The next step is to load the necessary crypto coins or tokens onto your wallet. You can do this at a crypto exchange or a broker like Bitpanda. Some networks require specific staking software or even running your own staking node.
After setting up, the actual crypto staking can begin. You can delegate your coins or tokens to a validator or run your own validator. In this direct form of staking, you should regularly monitor your staking activities to ensure a smooth and effective process.
Finally, keep an eye on the rewards and risks for your staked assets. Find out how often rewards are paid out and how you can claim them. At the same time, consider the market volatility and other risks associated with staking. Although direct crypto staking in a blockchain network can be complex, it allows you to contribute directly to the functionality and security of the network by validating blockchain transactions and creating new blocks.
How to get started with crypto staking
Are you investing in cryptocurrencies and holding coins and tokens based on a proof of stake blockchain? Then you can contribute to the network's security through staking and generate returns in the form of staking rewards by validating transactions.
There are different options for starting crypto staking. It is important to understand the conditions such as lock-in periods, minimum amounts, and reward structures of the various staking methods. Each option has its own advantages and limitations. The choice of provider and asset should be based on your individual needs and comfort level. With a crypto broker like Bitpanda, beginners and experienced traders can start staking quickly and easily, laying the foundation for passive income.
Frequently asked questions about crypto staking
Here answer the most commonly asked questions about staking:
Is Bitcoin (BTC) staking possible?
No, Bitcoin (BTC) staking is not possible as the Bitcoin network is based on a proof of work mechanism and not proof of stake. New Bitcoin can only be generated through mining, which involves verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems using computing power.
Which cryptocurrencies can I stake?
In principle, only crypto coins and tokens based on a proof of stake network can be staked. Cryptocurrencies on proof of work blockchains are generated through mining.
Do I need special hardware for staking?
For staking with crypto brokers or exchanges, you do not need special hardware. For direct crypto staking, some blockchain networks may require specific hardware or software.
Is staking worthwhile?
Staking can be worthwhile to generate passive income. By staking your crypto coins and tokens, you not only support the network but also earn rewards in the form of additional coins or tokens. These rewards can provide an attractive return on your held cryptocurrencies.
However, it is important to note that staking, like any investment, also carries risks, including market volatility. Therefore, it is essential to research carefully and make a well-informed decision.
More topics on crypto staking
Interested in a deeper dive into the topic? Our detailed articles offer further insights into the world of staking and show you what really matters.
This article does not constitute investment advice, nor is it an offer or invitation to purchase any digital assets.
This article is for general purposes of information only and no representation or warranty, either expressed or implied, is made as to, and no reliance should be placed on, the fairness, accuracy, completeness or correctness of this article or opinions contained herein.
Some statements contained in this article may be of future expectations that are based on our current views and assumptions and involve uncertainties that could cause actual results, performance or events which differ from those statements.
None of the Bitpanda GmbH nor any of its affiliates, advisors or representatives shall have any liability whatsoever arising in connection with this article.
Please note that an investment in digital assets carries risks in addition to the opportunities described above.